Collagen Supplements: Do They Work or are they just Modern-Day Snake Oil?
Posted by Guardian Athletic on Mar 10, 2021
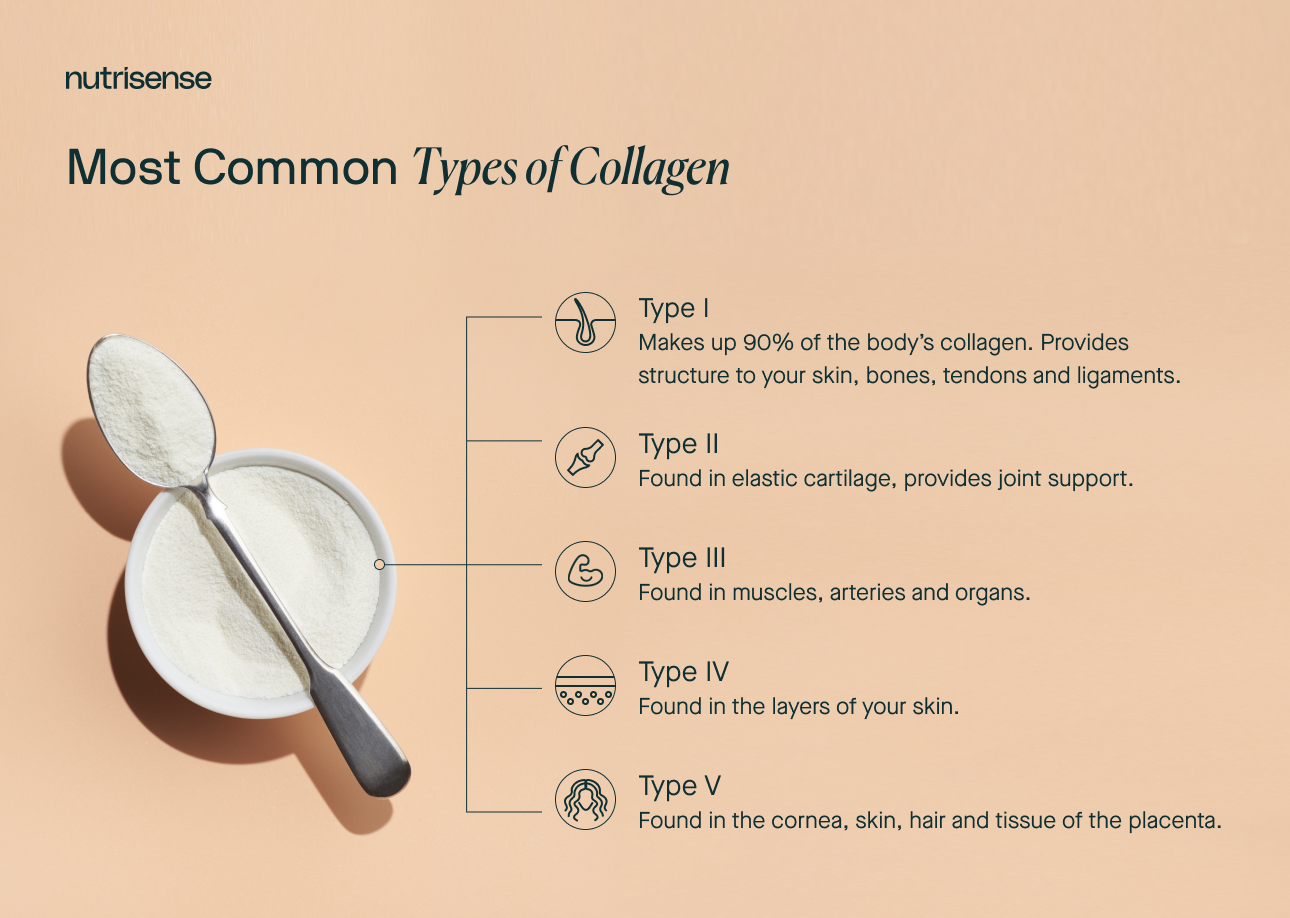
The health and beauty industry have exploded with collagen products; drinks, powders, capsules and creams - you name it, it’s out there. While collagen might be the latest beauty ‘must-have’ as 'skincare from within', there are a few things that every discerning collagen consumer must know.
Do Collagen Creams and Supplements Actually Do Anything?
When we talk about skin aging, we’re really talking about collagen—or, more accurately, a lack thereof. Pretty much every desirable characteristic of healthy skin comes down to collagen content: The more of this protein we have, the firmer, plumper, and juicier our skin looks.
Collagen is the body’s most abundant protein, made up of amino acids, or peptides. It literally glues our bones, cartilage, skin, and blood vessels together. It’s what makes our tissues grow, mature, and move. Its presence under your skin can keep it from sagging over time.
But as we age—and particularly if we smoke, drink, and get UV exposure while aging—our collagen production drops off, and the collagen we already have starts to break down. This causes wrinkles, as well as a loss of plumpness or fullness. Addressing these symptoms means addressing collagen loss in one way or another.
To that end, there is a slew of collagen-rich products on the market, most of which fall into one of two categories: moisturizers (particularly creams) and oral supplements. Trendy supplements dominate today’s market like collagen powders, while collagen creams are a bit more old school.
But regardless of the form the product takes, the manufacturers claim that giving your skin more collagen to work with will help it replenish what it’s lost, improving everything from hydration and elasticity to fine lines and wrinkles. However, experts remain skeptical.
Potential Health Benefits of Collagen Supplements
Because it makes up so many critical parts of our bodies, collagen is not only beneficial but essential to maintaining good health. However, the benefits of collagen supplements are still debated. While there is reasonable evidence that they help maintain hydrated skin and relieve osteoarthritis pain, more research is needed into less well-understood benefits, such as lowering blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
Here are some commonly cited benefits of collagen supplements:
1. Skin Elasticity and Hydration

As we age, our natural collagen production decreases leading to a gradual deterioration of our hair, skin, teeth and nails. You see this visibly in wrinkled skin or osteoporosis.
Collagen got its fame as a nonsurgical remedy in the beauty and health scene for combating wrinkles. It is thought to do this by forming fibroblasts (or specialized cell clusters on your dermis) which facilitate the growth of new cells. This helps replace dead skin with new youthful skin.
2. Collagen Helps You Digest Food Better

As stated above, collagen is a protein made up of a bunch of individual amino acids. The single most dominant amino acid in collagen is glycine. Think of glycine as a savior to your gut. Glycine is the master at regulating inflammation in your stomach, small intestine and GI tract.
Inflammation is caused in your gut when harmful toxins are able to pass through your digestive tract in your gut. These toxins in the form of food particles now have free rein to pass into your bloodstream, kicking off all sorts of inflammatory issues in your body.
Glycine helps reduce inflammation by forming connective tissue which protects the mucosal barrier of your gut. This helps tighten the tiny junctions in those suffering from leaky gut syndrome. It also has been shown to have other protective effects on the small intestine during injury and improves fructose mal-absorption.
3. Collagen Reduces Pain in Your Joints and Tendons
Everyone gets injuries at some point. They suck! But there is some good news about collagen with respect to joint, ligament and tendon injuries.
Well-designed studies are demonstrating that collagen hydrolysate shows an improvement in joint pain in athletes. A recent research is shows that collagen or gelatin taken with vitamin C assists in tendon repair and injury prevention.
4. Collagen Might Make You Live Longer

It is true that our western society consumes more meat than necessary for optimal health. Most of the meat we eat is awful for us. The popular notion to ‘eat less meat’ completely misses the point if the meat we do eat is still garbage.
This doesn’t even get into the environmental concerns, which is a topic for another day. For now, let’s talk about methionine. Methionine is the most abundant amino acid found in muscle meats like steak. It is essential because your body cannot make it from other things. It helps your liver detoxify drugs and make certain key molecules like the hormone adrenaline.
However, the often-ignored dark side of methionine is that it is toxic in high amounts. Animals who consume diets high in methionine die much younger than those eating less methionine. It follows that you should eat less methionine to live forever, right? Not so fast!
This is not necessary if you get enough of another amino acid called glycine which is shown to counteract the effects of methionine. Your liver needs glycine in order to effectively buffer out a surplus of methionine. So, the more chicken breast you eat, the more you should pay attention to your glycine intake to balance it out.
Glycine is one of the most important regulators of inflammation in your body. The typical western diet comes up short of the 8-10 grams needed daily. In addition to regulating inflammation in the liver, collagen also restores antioxidant status to promote longevity.
Glycine makes up one third of collagen, gelatin and also bone broth. If you eat lots of animal meat, consider eating higher quality (grass finished, pasture raised, etc.) and slightly less. Then you can add in collagen rich foods, gelatinous meats (animal skin, tendons, small bones, wings, oxtails etc.) and bone broth to balance out the methionine.
5. Collagen Helps You Sleep Better
Collagen is quietly being touted as a potent mood relaxer, sleep promoter and productivity booster. Human studies are showing that three grams of glycine (found in one collagen serving) taken before bed improves the quality of your sleep.
You might be wondering: does glycine knock me out like Xanax? No. Quite the opposite. You see, glycine decreases core body temperature and possibly inhibits muscle activity during REM sleep. Your body temperature naturally drops as bedtime approaches and continues to drop throughout sleep.This may be why glycine helps you sleep however; more research is needed.
6. Collagen Boosts Brain Health

Anything that helps you sleep better should be celebrated. That being said, the mood boosting effects of collagen extend further to brain health.
Not many are writing about this, but researchers are finding a positive impact on patients with schizophrenia who supplement with glycine as part of their regiment. Glycine is useful for treating the negative symptoms of schizophrenia: mainly depression and loss of mental fluency. It even improves psychotic symptoms in some cases. Since the negative symptoms of schizophrenia have such devastating effects on the sufferer's ability to function in the real world, the finding that glycine may help is significant.
The benefits of glycine on the brain may extend to other psychiatric and mood disorders. There are promising mechanisms to suggest that glycine assists with depression and neurodegenerative disease like Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s.
Keep in mind that it is early. However, there is lots to be excited about for collagen’s effects on productivity, cognitive disorders and neurodegenerative diseases.
7. Collagen Restores Antioxidants and May Protect You from Asthma
I’ll take a guess that you’ve heard how antioxidants are good for you. Everybody knows that. But how?
Antioxidants prevent oxidation. Oxidation leads to cell damage. Your body creates oxidants to fight off viruses and microbes. But if you produce too many then bad things happen: think cancer, heart disease, etc. Unless you live in a bubble, you’re also exposed to oxidants in your daily life. So you do your part by eating blueberries and maybe taking Vitamin C when you’re sick.
Glutathione is recognized as the master antioxidant in the cell. We are deficient due to environmental factors like stress, infections, aging, air pollution, GMO’s, etc. Researchers are showing that glutathione is an important predictor of longevity.
What Is The Best Time To Take Collagen?
If you’re having digestive or gut issues then the best time to take collagen is first thing in the morning on an empty stomach or with your meals.
For joint, tendon or ligament pain the best time to take collagen is approximately 1 hour before you exercise for best results (be sure to include 50 mg of vitamin c). The timing is crucial as your exercise activity helps to shuttle collagen peptides into your tendons and joints
For restful sleep, take collagen before bed for improved sleep quality.
To help control blood sugar, take 15 g of collagen before your meals. This will provide the 3-5 g of glycine necessary to help control your blood sugar response.
Should I Take Collagen Every Day?

No. You should start by incorporating more collagen rich foods in your diet, like bone broth. Food is medicine. From there you can experiment with taking collagen.
How long do you have to take collagen before you see results?
For ascetic benefits like skin health, studies usually show collagen takes 8 weeks to improve symptoms.
For joint and ligament pain or osteoarthritis, studies show that collagen can improve health outcomes in 3 months.
Check out Guardian Athletic's unique combination of 5 types of food sourced collagen combined with the amazing benefits of CBD. Combining the best of the best!
References
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/collagen-bene...
https://www.everydayhealth.com/skin-beauty/potenti...